Choosing the right serial communication standard is important. It affects how well a system works in real life. RS232, RS485, and RS422 each have special features. RS232 is good for short, one-to-one connections. RS485 can connect many devices over long distances. It is used a lot in factories. RS422 blocks noise well and works farther than RS232. More people are using these standards every year. Consumer electronics and factory machines use them the most.
Market Snapshot (2024):
Market Size
Projected 2031
Top Region
Main Use
$213 million
$370 million
Americas
Consumer Electronics
Quick Comparison
Summary Table

| Specification | RS232 | RS422 | RS485 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Transfer Type | Full duplex | Full duplex | Half duplex (2-wire), Full duplex (4-wire) |
| Maximum Distance | ~15 meters at 9600 bps | Up to 1200 meters at 9600 bps | Up to 1200 meters at 9600 bps |
| Number of Devices Supported | 1 (point-to-point) | 1 transmitter, up to 10 receivers | Up to 32 devices (expandable with repeaters) |
| Signaling Method | Single-ended | Differential | Differential |
| Voltage Levels | -15 V to +15 V | -6 V to +6 V | -7 V to +12 V |
| Topology | Point-to-point | Point-to-point | Multi-point |
| Wiring | 3 wires (TxD, RxD, GND) | 4 wires (2 twisted pairs) + GND | 2 or 4 wires + GND |
| Connector Types | DB9 or DB25 | Terminal block or DB9 | Terminal block or DB9 |
| Data Rate | Up to ~115 kbps | Up to 10 Mbps (short distances) | Up to 10 Mbps (short distances) |
| Noise Immunity | Lower (single-ended) | Higher (differential) | Higher (differential) |
| Typical Use Cases | PC-to-modem, printers, lab tools | Industrial automation, video, telecom | Industrial automation, building management, smart grids |
Key Differences
- RS232 can only connect one device to another. It is best for short cables, like from a computer to a printer. The wiring is simple, but it does not block noise well.
- RS422 lets one sender talk to ten receivers. It uses a special way to send signals that blocks noise. This helps the signal go farther. Factories and video systems use RS422 because it is steady and works over long cables.
- RS485 can link up to 32 devices on one network. It works in half-duplex and full-duplex. RS485 is good for places with lots of noise and long cables. That is why it is used in building controls and factories.
- RS232 sends signals in a simple way. RS422 and RS485 use a different way that blocks noise better. This makes RS422 and RS485 work farther and with less trouble from noise.
- RS485 lets many devices share the same wires. RS422 and RS232 do not let you do this.
Tip: When picking a serial standard, think about how many devices you need to connect. Also, think about how far the signal must go and if there is a lot of electrical noise.
RS232 Overview

RS232 How It Works
RS232 lets two devices talk to each other directly. It works both ways at the same time. You might use it to link a computer and a modem. The protocol uses positive voltage for a binary 0. It uses negative voltage for a binary 1. Data goes from the sender’s buffer through a cable. Then it reaches the receiver’s buffer. Devices use pins like DTR and DSR to check if they are ready. RTS and CTS help control the flow of data. This stops data from getting lost. RS232 sends data one byte at a time. Each byte has start and stop bits. Devices do not need a shared clock to talk.
Technical Specs
| Parameter | Specification |
|---|---|
| Voltage Levels (Mark) | -5V (min) to -15V (max) |
| Voltage Levels (Space) | +5V (min) to +15V (max) |
| Maximum Cable Length | 50 feet (approx. 15 meters) |
| Maximum Data Rate | 20 kbps at 50 feet; up to 1 Mbps max |
| Connector Types | DB9, DB25 |
| Signaling Method | Single-ended, asynchronous |
The chart below shows that longer cables mean slower speeds. If you want fast data, you need a short cable.
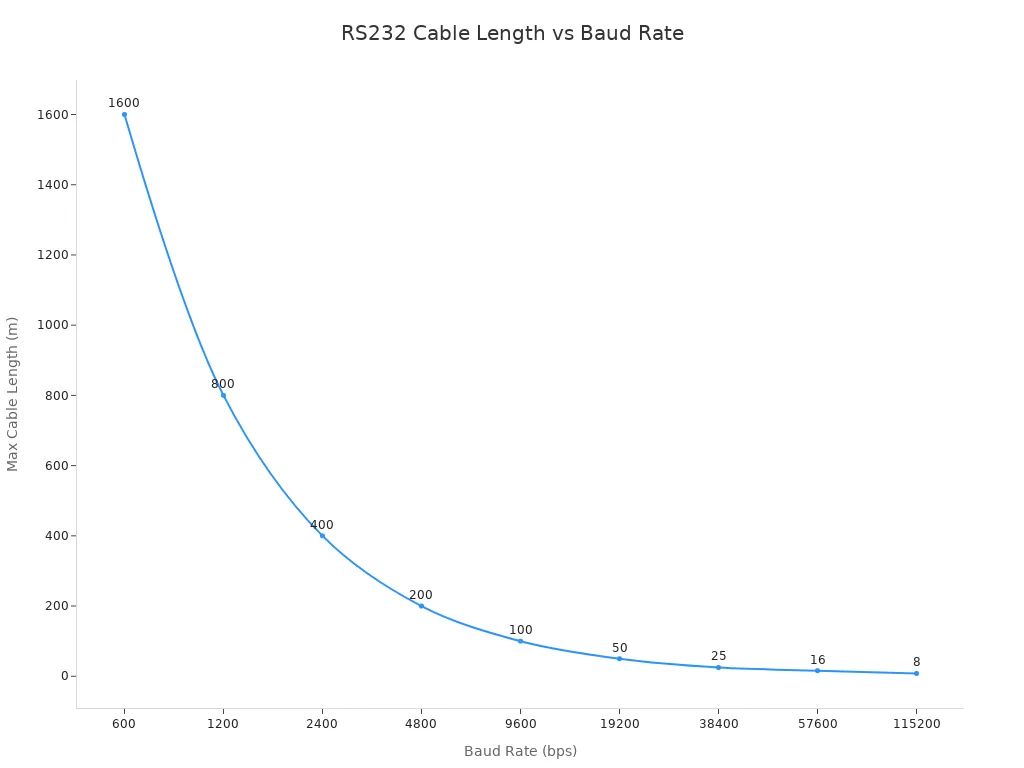
Pros and Cons
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
| Simple and easy to use | Limited speed compared to modern protocols |
| Widespread compatibility | Short communication range (≤ 50 feet) |
| Reliable for point-to-point connections | Susceptible to electrical noise |
| Low cost and widely available | No power supplied over the connection |
Use Cases
- Factories use RS232 to connect PLCs to machines.
- Data systems use RS232 to watch things in real time.
- Phone systems use RS232 for modems and switches.
- Hospitals use RS232 for medical device checks.
- Stores use RS232 for barcode scanners and printers.
- Planes and cars use RS232 to move data for tests.
Real-World Example
You can use RS232 to link a computer to a lab tool or modem. The computer sends commands through the RS232 port. The device sends data back to the computer. This setup is good when only two devices need to share information.
RS485 Basics

RS485 How It Works
RS485 sends data using two wires with opposite signals. The receiver checks the difference between these wires. This helps block out electrical noise. RS485 lets devices take turns sending data. Only one device can send at a time. This stops data from crashing together. RS485 works well when devices are lined up on one cable. You can connect up to 32 devices on one bus. Some new chips let you connect up to 256 devices. Using shielded cables and special transceivers keeps signals safe and clear.
- RS485 is not a protocol. It is an electrical standard. Many protocols, like Modbus, use RS485 for connections.
- RS485 can handle ground differences between devices. This makes it work well in big buildings or factories.
- Drivers stop sending when not in use. This keeps the bus safe and avoids damage.
Technical Specs
| Specification Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
| Maximum Cable Length | Up to 4000 ft (1.2 km) at 100 kbps |
| Maximum Data Rate | 10 Mbps at short distances (40 ft / 12 m) |
| Device Support | Up to 32 devices (standard), up to 256 with modern transceivers |
| Signaling Method | Differential (twisted pair, 100-120 Ω termination) |
| Communication Mode | Half-duplex (2-wire), Full-duplex (4-wire with extra pair) |
| Voltage Range | -7V to +12V common-mode |
Pros and Cons
| Benefits | Limitations |
|---|---|
| Long cable runs up to 1200 meters | Half-duplex limits simultaneous send/receive |
| Connects many devices on one bus | No power supplied over the data line |
| Excellent noise immunity | Lower data rates at long distances |
| Cost-effective and easy to install | Needs careful wiring and termination |
| Tolerates ground potential differences |
Tip: RS485 works best with the right cable and shielded wires. This setup keeps signals strong and helps stop errors.
Use Cases
- Factories use RS485 to connect sensors, controllers, and machines.
- Building systems use RS485 for HVAC, lights, and security.
- Smart meters and energy grids use RS485 to collect data.
- Traffic and train systems use RS485 for safe signals.
- Many industrial devices use RS485 to talk to a main computer.
Real-World Example
A factory often uses RS485 to link many temperature sensors to one controller. The sensors send data over one twisted-pair cable. The controller gets all the readings in real time. This setup saves money on wires and keeps data safe, even with lots of electrical noise. Many factories use the Modbus protocol with RS485 to connect devices from different brands. This makes it easy to add more devices and control them over large areas.
RS422 Essentials

RS422 How It Works
RS422 sends data using two wires for each signal. Each wire has a matching return wire. This helps block out electrical noise. The signal stays strong over long cables. One device is the transmitter. It can send data to up to ten receivers at once. RS422 can send and receive data at the same time if you use four wires. Devices can talk both ways at once with this setup. Only one transmitter can be on the line. This stops data from crashing together. It keeps messages clear. RS422 works well for long cables and fast speeds. It is a good choice for building controls and TV studios.
Technical Specs
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Maximum Distance | 1,200 meters (3,900 feet) |
| Maximum Devices | 1 transmitter, up to 10 receivers (standard); up to 31 with modern chips |
| Data Rate | Up to 10 Mbps (short cables) |
| Cable Type | Twisted pair (often shielded) |
| Topology | Point-to-multipoint (simplex or full-duplex) |
Pros and Cons
| Strengths | Weaknesses |
|---|---|
| Long cable runs (up to 1,200 meters) | Supports fewer devices than RS485 |
| High data rates (up to 10 Mbps) | More wiring needed (4 wires for full-duplex) |
| Good noise immunity (differential signaling) | Medium noise immunity compared to RS485 |
| Full-duplex possible | Only one transmitter per line |
Use Cases
- Factories use RS422 to link controllers and sensors.
- Building systems use RS422 for remote panels and monitors.
- TV studios use RS422 for video and camera control.
- RS422 helps send data far in telemetry systems.
Note: RS422 is best when you need to send data far. It works well when you do not need much feedback.
Real-World Example
A building manager uses RS422 to connect a main control unit to many sensors and panels. The control unit sends commands over long cables. Each sensor gets the data clearly, even with lots of electrical noise. This setup lets managers control lights, HVAC, and security from one place. RS422 keeps the data fast and reliable, even in big buildings.
Direct Comparison
Distance and Speed
Distance and speed matter a lot in serial communication. Each standard has its own limits. RS232 works best for short cables. It can reach about 15 meters (50 feet) at normal speeds. RS422 and RS485 can send data much farther. Both can reach up to 1200 meters (about 4000 feet) at lower speeds. When the cable gets longer, the speed drops. At short distances, RS422 and RS485 can reach up to 10 Mbps. RS232 usually tops out at 115 kbps.
| Protocol | Max Distance | Max Data Rate | Duplex Mode | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| RS232 | ~15 meters (50 ft) typical | Up to 115.2 kbps | Full duplex | Point-to-point |
| RS422 | Up to 1219 meters (4000 ft) | Up to 10 Mbps (short cables) | Full duplex | One transmitter, up to 10 receivers |
| RS485 | Up to 1200 meters (4000 ft) | Up to 10 Mbps (short cables) | Half duplex | Up to 32 devices |
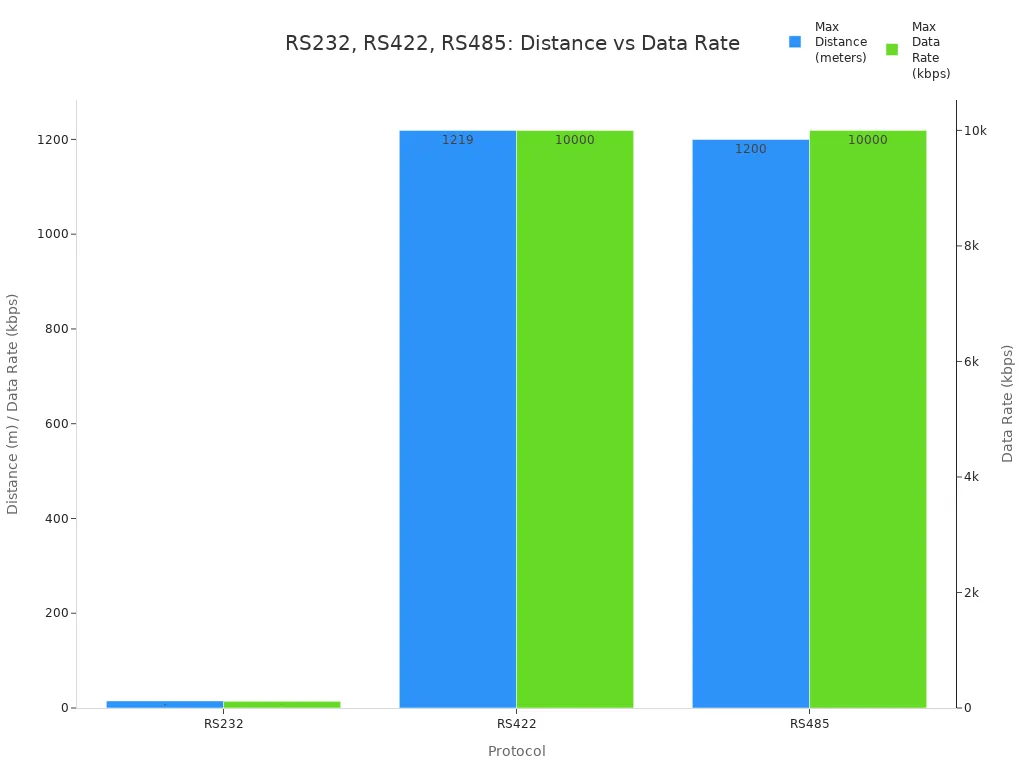
Tip: For long cables or high speeds, RS422 and RS485 work better than RS232.
Wiring and Topology
Wiring and network shape affect how devices connect. RS232 uses at least three wires: transmit, receive, and ground. It only connects two devices in a point-to-point setup. RS422 uses four wires, with two twisted pairs. One pair sends data, and the other receives. This allows full duplex communication. RS422 supports one transmitter and up to ten receivers. RS485 uses two wires for half duplex or four wires for full duplex. It supports a bus topology, letting up to 32 devices share the same cable. Both RS422 and RS485 need special resistors at the ends of the cable to keep signals clear.
| Standard | Wiring Requirements | Network Topology | Communication Mode | Max Distance | Number of Devices |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RS232 | 3 wires (Tx, Rx, GND) | Point-to-point | Full duplex | ~15-20 meters | 2 devices |
| RS422 | 4 wires (2 twisted pairs) | Point-to-multipoint | Full duplex | Up to 1200 meters | 1 transmitter, up to 10 receivers |
| RS485 | 2 wires (1 twisted pair) | Multi-drop (bus) | Half duplex | Up to 1200 meters | Up to 32 devices |
- RS232: Simple wiring, only two devices.
- RS422: Four wires, one sender, many receivers.
- RS485: Two wires, many devices, bus shape.
Note: RS485 networks should avoid star shapes and long side branches. This keeps the signal strong.
Noise Immunity
Noise can ruin data. RS232 uses single-ended signaling. It sends data as a voltage between one wire and ground. This makes it easy for noise to get in. RS422 and RS485 use differential signaling. They send data as a voltage difference between two wires. If noise hits both wires, the receiver cancels it out. This makes RS422 and RS485 much better in noisy places like factories.
RS422 and RS485 handle electrical noise much better than RS232. They work well over long cables and in places with lots of machines.
Scalability
Scalability means how easy it is to add more devices. RS232 does not scale well. It only connects two devices. RS422 allows one sender and up to ten receivers, but only one device can send. RS485 supports up to 32 devices on one cable. Some new chips let even more devices join. This makes RS485 the best choice for big networks.
- RS232: Only two devices, not scalable.
- RS422: One sender, up to ten receivers, limited scalability.
- RS485: Up to 32 devices, very scalable for large systems.
Application Scenarios
Each standard fits different jobs. RS232 works well for simple, short connections like linking a computer to a printer. RS422 fits jobs that need fast, long-distance data to many receivers, such as video systems or building controls. RS485 shines in big networks with many devices, like factory automation or building management. It handles noise and distance well.
| Scenario | Best Standard |
|---|---|
| Short, simple link | RS232 |
| Long distance, one-to-many | RS422 |
| Many devices, noisy place | RS485 |
RS485 is the top pick for industrial automation and building management. RS422 works well for fast, long runs to several receivers. RS232 is best for simple, direct device links.
Choosing the Right Standard
Key Factors
Picking the right serial communication standard depends on a few things. Every system needs something different. The table below shows what engineers and technicians should look at:
| Factor | RS232 | RS422 | RS485 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Communication Topology | Point-to-point only | Multi-drop (1 driver, multiple receivers) | True multi-point (multiple drivers and receivers) |
| Wiring Complexity | 2 wires (single-ended) | 4 wires (differential, separate Tx/Rx) | 2 wires (differential, half-duplex) |
| Distance Limitations | Up to 50 ft (15 m) | Up to 500 ft (150 m), longer with repeaters | Up to 1200 m at 9600 bps |
| Noise Immunity | Low (single-ended, susceptible) | High (differential signaling) | High (differential signaling) |
| Number of Devices | 1 device per port | Up to 32 devices | Up to 128 transceivers |
| Duplex Mode | Full duplex | Full duplex | Typically half duplex |
| Programming Complexity | Simple | Simple (separate Tx/Rx lines) | More complex (must manage transmitter enable/disable) |
| Hardware Availability | Widely available on PCs | Requires special ports or converters | Requires special ports or converters |
Engineers also need to think about where the system will be used. Some places have lots of electrical noise. Factories and big buildings often need longer cables and more devices. The next table shows how each standard deals with noise and distance:
| Standard | Environmental Noise Immunity | Maximum Communication Distance | Key Characteristics |
|---|---|---|---|
| RS232 | Low; susceptible to noise over longer cables | ~15 meters | Uses voltage signaling; limited by noise at high bit rates and longer distances |
| RS422 | High; balanced differential signaling | Longer than RS232 (up to ~1200 meters) | Balanced interface reduces noise by using voltage difference between two lines |
| RS485 | High; balanced differential signaling | Up to 1200 meters | Supports multi-point networks; best for noisy environments and long distances |
Tip: Always check how many devices you need, how long the cable is, and if there is a lot of noise. These things help stop data loss and errors.
Decision Guide
It is easier to pick the right standard if you follow steps. This guide helps match your needs to the best choice:
- How many devices need to connect?
- Only two devices: Use RS232.
- One sender, several receivers: Choose RS422.
- Many devices sharing one cable: Pick RS485.
- How far does the signal need to travel?
- Short distance (under 15 meters): RS232 works well.
- Medium to long distance (up to 1200 meters): RS422 or RS485 are better choices.
- Is the environment noisy?
- Low noise: RS232 may be enough.
- High noise (factories, industrial sites): RS422 or RS485 provide better protection.
- What is the required speed?
- Low to moderate speed: All three standards can work.
- High speed over long cables: RS422 or RS485 handle this best.
- How complex is the wiring and setup?
- Simple, direct connection: RS232 is easiest.
- More devices or longer runs: RS422 and RS485 need more planning and careful wiring.
 Quick Reference Table:
Quick Reference Table:
| Scenario | Recommended Standard |
|---|---|
| Simple, short, direct connection | RS232 |
| Long distance, one-to-many communication | RS422 |
| Many devices, long distance, noisy area | RS485 |
Note: RS485 can connect the most devices and reach the farthest. RS422 is fast and blocks noise well for fewer devices. RS232 is the easiest for short, simple links.
This guide helps engineers and technicians pick the right serial communication standard for any job. Good planning makes sure data moves safely and the system works well.
Picking the right serial communication standard changes how a system works and is fixed. The table below shows the main differences:
| Standard | Topology | Max Distance | Devices Supported | Noise Immunity | Maintenance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RS232 | Point-to-point | ~15 meters | 2 | Low | Simple |
| RS422 | Point-to-multipoint | 1200 meters | 10 | High | Moderate |
| RS485 | Multi-point | 1200 meters | 32 | High | Complex |
Engineers should use RS232 for easy, short connections. RS422 is better for long cables where noise is a problem. RS485 works best for big networks with lots of noise. If you want to learn more, check out SparkFun tutorials or Altium articles. These resources give helpful tips and expert advice.
RCOMPT Industrial Panel Computer RS232 Interface Highlights

Professional Design
- Native RS232 controller, not USB adapter
- Standard DB9 interface with locking screw
- Independent power supply to avoid interference
Industrial Protection
- ±15kV ESD protection
- 2500V optical isolation
- Corrosion-resistant gold-plated contacts
Stable Transmission
- Supports 300bps to 1Mbps
- Transmission distance up to 100 metres
- Supports hot-swappable plugging and unplugging
The RCOMPT RS232 interface has passed rigorous industrial environment testing to ensure long-term stable connectivity with various industrial devices.
FAQ
What is the main reason to choose RS485 over RS232?
RS485 supports longer cables and more devices. It works well in noisy places like factories. RS232 only connects two devices and works best for short distances.
Can RS232, RS422, and RS485 cables be used interchangeably?
No, each standard uses different wiring and signaling. Devices may not work or could get damaged if connected with the wrong cable. Always match the cable to the standard.
Why do RS422 and RS485 handle noise better than RS232?
RS422 and RS485 use differential signaling. This method cancels out electrical noise. RS232 uses single-ended signaling, which does not block noise as well.
How many devices can connect to an RS485 network?
RS485 supports up to 32 devices on one bus. Some modern chips allow even more. This makes RS485 a good choice for large networks.
Do these standards supply power to connected devices?
No, RS232, RS422, and RS485 do not provide power through the data lines. Devices need their own power sources.


